 |  |
|
Northern Bobwhite - Colinus virginianus Sole representative of ODONTOPHORIDAE in NC | Search Common: Search Scientific: |
|
|
|||||||
| General Comments | The state's only quail species has suffered the opposite fate of the Wild Turkey. Whereas Bobwhites were once one of the state's most common birds, with observers often recording 30-50 on the 50-stop Breeding Bird Survey routes, the species has shown severe declines throughout its range since about 1980, owing presumably to an increase in mammalian predators and probably to loss of farmland and associated early succession habitat. However, other factors certainly are involved, as many other early succession associates of the Northern Bobwhite in the same habitats are holding steady or increasing; however, the ones doing better nest up in shrubs and saplings, well off the ground. Fire ants have often been mentioned as one of these additional factors that impact nesting quail (as the quail nests are placed on the ground). Sadly, quail do not fare well in captive breeding programs, and thus improvements in quail numbers must take the tedious route of working with farmers and other landowners (including public agencies) to better manage their lands for this species -- as opposed to captive breeding and releases that have helped the Wild Turkey population. For breeding, Bobwhites favor dense cover of young clearcuts, brushy overgrown fields, woodland borders, and open woods with some cover. At other seasons, they tend to move more into forest edges and open forests, very dense brier thickets, and other heavy cover. Because they often gather into coveys up to 10-20 birds in winter, and they become very quiet at this season (seldom calling except at dawn and dusk), it can be quite difficult to encounter a flock in a day of birding, and many CBC's now often miss the species completely, even though sizable numbers are likely present in the count circle. | ||||||
| Breeding Status | Breeder | ||||||
| NC BRC List | Definitive | ||||||
| State Status | |||||||
| U.S. Status | |||||||
| State Rank | S4S5 | ||||||
| Global Rank | G4G5 | ||||||
| Coastal Plain | Permanent resident; non-migratory. Formerly common to very common throughout, except absent on the Outer Banks (except Bodie Island); currently fairly common at best, and declining. Peak counts: ? | ||||||
| Piedmont | Permanent resident; non-migratory. Formerly common to very common essentially throughout, though less numerous in the foothills; now, generally uncommon, and still declining. Very scarce now in highly urbanized counties. Peak counts: ? | ||||||
| Mountains | Permanent resident; non-migratory. Formerly mostly fairly common, and common locally, and even ranged upwards to over 6,000 feet. Currently, mostly uncommon; declining. In winter, withdraws downward, seldom found over 4,000 feet in the colder months. Peak counts: ? | ||||||
| Finding Tips |
Though the species is much harder to find than 10 to 20 years ago, Bobwhites should still be HEARD in a given morning in late spring and summer, in somewhat remote areas away from human habitation, usually in small numbers. It is a matter of driving back roads, making many stops, and listening; they are out there, but certainly are not numerous now. Seeing Bobwhites may require some luck, as usually birders simply stumble onto a covey along a wooded edge, or see one or a few scurrying across a dirt track. ** to *** | ||||||
| Attribution | LeGrand[2023-03-02], LeGrand[2018-02-01], LeGrand[2012-01-01] | ||||||
| NC Map Map depicts all counties with a report (transient or resident) for the species. | Click on county for list of all known species. |
| NC Breeding Season Map Map depicts assumed breeding season abundance for the species. | 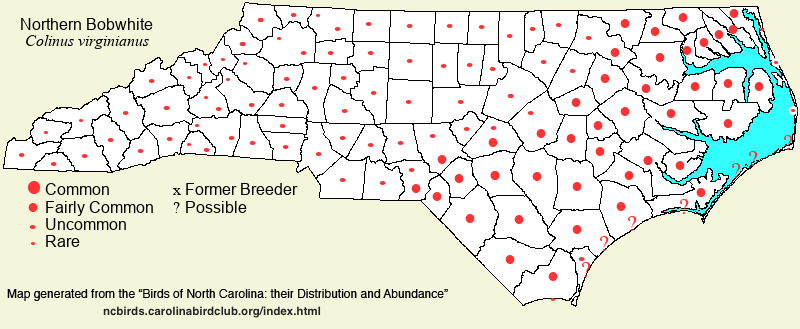 |